Establish a projected income statement: Free Excel template to download
Amber Baynaud
•
Jul 8, 2024
Today, the forecast income statement is one of the most important financial statements for preparing a business plan and assessing the profitability and financial health of a company. In addition, it helps anticipate the company's inflows and outflows reflecting the level of its economic activity for a period called the financial year. With a forecast income statement, it is possible to determine whether the company's activity generates profits or losses and whether this activity constitutes a viable project or not. But what is a forecast income statement and why should it be prepared? What does it consist of ? How to build it and how to analyze it? Qotid answers all these questions in this article.
What is a forecast income statement?
The forecast income statement is presented in the form of a financial table and appears in the financial part of the business plan. In the context of starting a business, it allows managers to make financial assumptions over several years (generally between 3 and 5 years).
But why is it essential today to prepare a forecast income statement?
First of all, the forecast income statement is important during the launch phase of a business. This document is part of the forecast financial plan and is a tool that can be requested by investors or the bank. It informs them about the viability of the project and the interest they have in trusting the newly established company.
The forecast income statement also allows investors to identify not only the profits or losses incurred by the company but also the different methods implemented to achieve these results. During a fundraising campaign, for example, investors may want to know if the amount of dividends distributed will meet their expectations.
Finally, regularly maintaining a forecast income statement simply allows managers to monitor the financial health of their company. They will be able to check if expenses are not too significant compared to revenues, or if the company's activity generates profitability. They can thus make the best decisions and anticipate potential difficulties.
How is the forecast income statement structured?
The forecast income statement lists all expenses (costs) and revenues (income) of the company.
We can distinguish three categories of costs and revenues:
Operating costs and revenues
Operating costs
These operating costs correspond to the expenses incurred by the company to ensure the operation of its activity. These expenses can include purchases of goods, stock variations, personnel costs, or depreciation provisions.
Operating revenues
Operating revenues are mainly made up of sales (service provisions, sales of goods, production sold). This represents the sales volume generated by the company's activity.
Financial costs and revenues
Financial costs
Financial costs may include interest on a loan taken out with a bank, for example. After obtaining financing, the company will pay interest that will be reflected in this part of the forecast income statement.
Financial revenues
Financial revenues can be the interests generated from investments or placements.
Exceptional costs and revenues
Exceptional costs
Exceptional costs are all other costs that are not related to the regular activity of the company and that occur exceptionally. These may include fines, financial penalties, penalties, etc.
Exceptional revenues
Exceptional revenues are all receipts obtained that are not part of the company's operating cycle and arise from unexpected events: customer penalties, tax relief.

How to create a forecast income statement?
The preparation of a forecast income statement consists of three main steps:
Determining revenue
Evaluating forecasted costs
Calculating forecasted results
Determining revenue
Determining your forecast revenue is an essential step in the forecast income statement. If you are starting a company, you can base your estimates on the revenue figures of competitors to set yours. If you have already had several financial years, you can potentially base it on the revenue figures from previous years, adding a growth rate if you feel it is necessary.
To get a more accurate idea of your company's forecast revenue, it is useful to conduct a market study beforehand. Why? First of all, this study would allow you to position yourself relative to your competitors, in terms of pricing, for example. With this positioning, you could determine your potential sales volume for the upcoming years. Additionally, it will allow you to identify your various clients: their habits, their needs, their familiarity with the company's activity. This way, you could determine whether your sales will increase or decrease depending on your products and customer expectations.
Finally, you will need to consider any aids and subsidies that the company may be entitled to, which will obviously affect your revenue amount.
To calculate your forecast revenue, you just need to perform this calculation:
(quantity of A * selling price of A) + (quantity of B * selling price of B) + etc.
In addition, do not forget to add any various subsidies received to the total revenue sources.

Evaluating forecasted costs
When forecasts on revenue are made, it is necessary to establish forecasts regarding the various costs. Depending on the anticipated revenue, expenses may be substantial. As mentioned earlier, forecasted costs are classified into three categories:
Operating forecasted costs
Financial forecasted costs
Exceptional forecasted costs
Operating forecasted costs
There are again three types of operating forecasted costs:
Fixed forecasted costs:
These are costs that do not vary with the company's activity (rent, insurance fees, subscriptions, etc.)
Variable forecasted costs:
These are costs that vary according to the company's activity (purchases of goods, travel expenses, etc.)
Semi-variable forecasted costs
These are costs that have a fixed part and a variable part (salaries composed of a fixed amount and a commission or bonuses).
Financial forecasted costs
Financial forecasted costs are linked to the financial operations of the companies such as:
Loan interests or other financial debts
Interests related to bank overdrafts
Discounts granted to clients
Etc.
Exceptional forecasted costs
Exceptional forecasted costs are all costs that do not fall under the operating cycle of the company or financial operations. These costs often occur during unexpected events like penalties, fines, unrecoverable debts, etc.

Calculating forecasted results
The main objective of the forecast income statement is to verify that the forecast revenue covers all the forecasted expenses. Once the revenue and forecasted costs are established, it is possible to determine this result. How to calculate these different results?
Operating result
This is the result directly related to the company's activity.
Operating result = operating revenues (not just the revenue!) - operating costs
Financial result
This is the result related to the company's financial operations.
Financial result = financial revenues - financial costs
Current result
This result focuses on the company's ongoing activities. This indicator is often used for forecasting future profitability. It takes into account all operations normally conducted by the company, whether it concerns its debt or the interests derived from its investments.
Current result = operating result + financial result
Exceptional result
This is the result related to the exceptional events that the company has faced.
Exceptional result = exceptional revenues - exceptional costs
Net result
This result corresponds to the sum of all results. When a company has a positive net result, it means that all of its revenues cover its costs and that it generates a profit. If this result is negative, then the costs are too significant compared to the revenues earned, and the company incurs a loss.
When this result is positive, the company may be subject to corporate tax and possibly a share of profits for employees.
Net result = current result + exceptional result - corporate tax - employee profit sharing
How to analyze a forecast income statement?
Although the primary objective of the forecast income statement is to analyze profitability, it also highlights several financial indicators whose analysis is essential for the growth and sustainability of a company.
Operating margin
This derived from the income statement can sometimes be directly presented in it. It shows the percentage share taken by the result related to the company's ongoing activities compared to the revenue.
Operating margin = operating result / revenue
Gross Operating Surplus (EBE)
EBE stands for Excédent Brut d’Exploitation. It is a crucial indicator observed by business leaders as it helps to determine whether a company has a profitable operation. If this balance is positive, then it is. If it is negative, then it is not. This indicator appears in the intermediate management balances and shows the profitability of a company while considering only its income and expenses related to its operating cycle.
EBE = Revenue + operating subsidies - consumed purchases - third-party consumption - taxes - personnel costs
Cash-Flow Capacity (CAF)
The CAF or Capacity for Self-Financing is a ratio calculated to determine whether a company is capable of financing its operating cycle independently.
CAF = net result for the fiscal year + calculated costs - calculated revenues + net book value of divested assets - revenues from asset disposals.
Many indicators can be used in addition to those presented to help businesses gain maximum knowledge about the resources they hold, the financing necessary to cover their operating cycle, or their minimum activity level to achieve.
Projected income statement or differential?
Unlike the forecast income statement, the differential income statement distinguishes between fixed costs and variable costs of a company. It is an essential tool in management control that can define the breakeven point of the company, as well as its margin on variable costs, variable costs, fixed costs, safety margin, break-even point, etc.
The differential income statement acts as a predictive management tool as it measures the contribution of each product to the result.
With this income statement, companies will be able to measure the minimum activity level required to fully cover fixed costs, study the contribution of each product to wealth creation and the coverage of fixed costs, and make financial projections.

What is the difference between the balance sheet and the income statement?
The balance sheet and the income statement are two accounting and financial documents, mandatory for certain companies, that can sometimes be confused or used awkwardly. First of all, the income statement. The income statement serves to track the company's activity. It lists and analyzes all the expenses and revenues necessary for the proper functioning of the company over a given period. It allows monitoring the evolution of the company's inflows and outflows during this period.
As for the balance sheet, it is used to present the company's assets at a specific point in time. We can distinguish two parts: assets and liabilities.
Assets: what the company possesses
This can include fixed assets (tangible, intangible, financial). These are the investments made by the company with a view to successfully carrying out its activities.
It may also encompass what are called “current assets”. These are stocks, accounts receivable, or cash.
Liabilities: the company's debts
We can find in the liabilities of the balance sheet: capital, equity, net income for the fiscal year, reserves, and debts (tax, social, or operational).
Therefore, these two documents do not present the same elements and do not meet the same needs. One presents a static view of the company's assets, and the other a dynamic view of the financial flows tracing the company's activity.


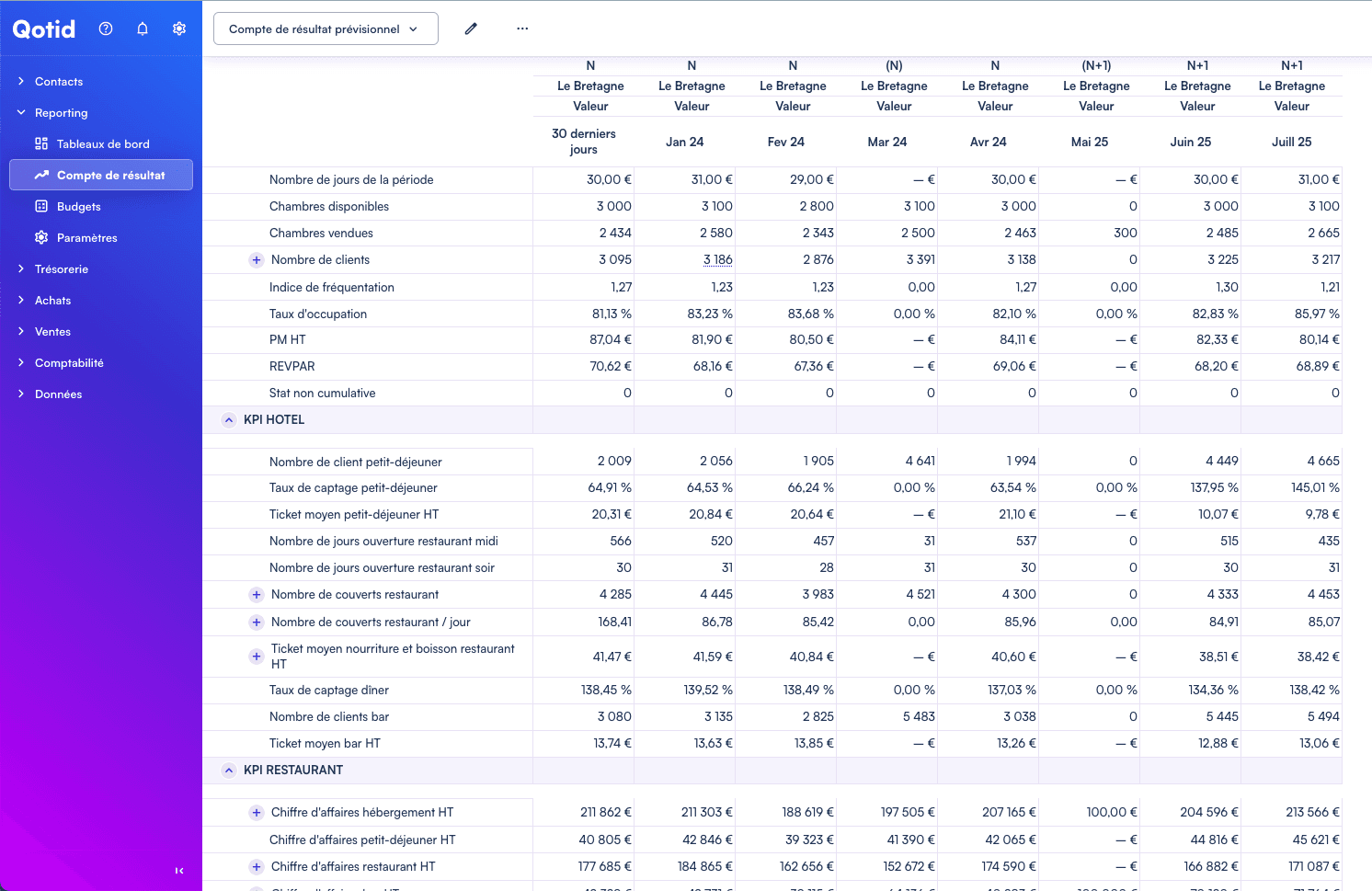
Excel model of a forecast income statement
Note that the forecast income statement can change and adapt according to the context of the company. Here, we offer a basic model that you can modify and adjust to fit the needs of your business perfectly.

In summary
The forecast income statement is an important financial table for the creation and management of a business. It allows for making financial assumptions over several years and determining if the company's activity is viable and profitable. It consists of three categories of costs and revenues: operating costs and revenues, financial costs and revenues, and exceptional costs and revenues. To build a forecast income statement, one must determine the forecast revenue, evaluate the forecasted costs, and calculate the forecasted results. Its analysis highlights several important financial indicators for the growth and sustainability of the company. There is also a differential income statement that complements the forecast income statement and allows the distinction between the company's fixed and variable costs. Finally, one should not confuse the income statement that traces the company's activity over a given period with the balance sheet, which presents the company's assets at a specific moment in time.
F.A.Q :
What is a forecast income statement?
The forecast income statement is an important financial table for the creation and management of a business. It allows for making financial assumptions over several years and determining if the company's activity is viable and profitable.
What does a forecast income statement consist of?
The forecast income statement consists of three categories of costs and revenues: operating costs and revenues, financial costs and revenues, and exceptional costs and revenues.
How to build a forecast income statement?
To build a forecast income statement, one must determine the forecast revenue, evaluate the forecasted costs, and calculate the forecasted results.